BASIC INFORMATION
What’s Japan like? How to get a job in the nursing care field in Japan?
Let us introduce the basic information about Japan and four different types of status of residence to work as a care worker.
ABOUT KAIGO

Nursing Care Facilities and Nursing Care Benefits in Japan※
- Long-Term Care Insurance Facilities:
- 13,409
- Nursing Care Service Companies:
- 363,452
- ※Results of ‘Survey of Institutions and Establishments for Long-term Care’ (2018), ‘Annual Report on Nursing Care Insurance: Business Report’ (2018) by the Japan Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare
Status of Residence for Nursing Care
Features of Four Systems for Status of Residence
To work in the nursing care field, there are four systems for status of residence: ‘EPA (Economic Partnership Agreement)’ started in 2008; ‘Nursing Care’ and ‘Technical Intern Training’ started in 2017; Specified Skilled Worker started in 2019.
| EPA | Nursing Care | Technical Intern Training | Specified Skilled Worker | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Status of Residence | 'Designated Activities' | 'Nursing Care' ※4 | 'Technical Intern Training (i)-(iii)'※7 | 'Specified Skilled Worker (i)' |
| Purpose of System | Acceptance for the purpose if acquiring Certified Care Worker national qualification and enhancement of international cooperation | Acceptance of international workers in specialist/technical areas | Transfer of skills from Japan to another country | Acceptance of foreign nationals with specific expertise/skills to address labor shortage |
| Operationg Country | Indonesia, the Philippines, Vietnam | No limitation | No limitation | No limitation |
| Period of Residence | 4 years(No limitation after obtaining a Certified Care Worker qualification) | No limitation | 5 years maximum ※8 | 5 years maximum ※8 |
| Accompaniment of Family Members | Family members(spouse/child)※1 | Family members(spouse/child) | N/A | N/A |
| Japanese Language Skills | N3 ※2 | N2 ※5 | N4 | CFER2、Japanese language skills necessary for working in long-term care※10 |
| Qualification and Study Experience in Their Home Country | Graduate of nursing related school or has government certification as care worker in home country | Depending on the individual | Depending on the supervising organizations | Individual with specific knowledge/skills ※11 |
| Requirement to Take Certified Care Worker National Examination | Yes ※3 | Yes ※6 | N/A ※9 | N/A ※9 |
| Acceptance Support and Support Organizations | JICWELS(International Welfare Agency) | N/A | Each supervising organization | Registered supporting organizations |
- ※1After obtaining a Certified Care Worker qualification.
- ※2Requirements at time of entry for the Philippines: N5 or higher level, Indonesia: N4 or higher level, Vietnam: N3 or higher level.
- ※3As an exception, individuals who fail the exam but satisfy certain scores may have residence extended for one year only and take the examination again.
- ※4Provided. However, ‘Student’ before obtaining a Certified Care Worker qualification.
- ※5Some schools require N2 or higher level.
- ※6Individuals who graduated between April 2017 and March 2022 can obtain a Certified Care Worker qualification either by passing the national examination within five years, or engaging in long-term care for five years after graduation.
- ※7Year 1: ‘Technical Intern Training (i)’ Year 2-3: ‘Technical Intern Training (ii)’ Year 4-5: ‘Technical Intern Training (iii)’
- ※8Provided. However, the status of residence ‘Nursing Care’ can be selected when certification is obtained, enabling permanent employment. A technical intern trainee who completed the third year is exempted from the examination for obtaining ‘Specific Skilled Worker (i)’ (if the status of residence is changed, the maximum period of residence becomes ten years, with technical intern and specified skills).
- ※9Status of residence may be converted to ‘Nursing Care’ by obtaining a Certified Care Worker qualification.
- ※10Must pass ‘Japan Foundation Test for Basic Japanese (JFT-Basic)’ developed by The Japan Foundation, and ‘Nursing Care Japanese Language Evaluation Test’ developed by the Japan Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. An individual with JLPT N4 or higher level is exempted from JFT-Basic.
- ※11Must pass ‘Nursing Care Skills Evaluation Test’ developed by the Japan Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare.
The Steps Required until Recruitment
According to a status of residence chosen, the steps you need to take until recruitment differ. If you obtain ‘EPA’ or ‘Nursing Care’ with a national qualification for Certified Care Worker, you can work permanently in Japan. As for ‘Technical Intern Training’ and ‘Specified Skilled Worker,’ you will be able to utilize the skills you obtained while you were staying in Japan when you go back to your country.
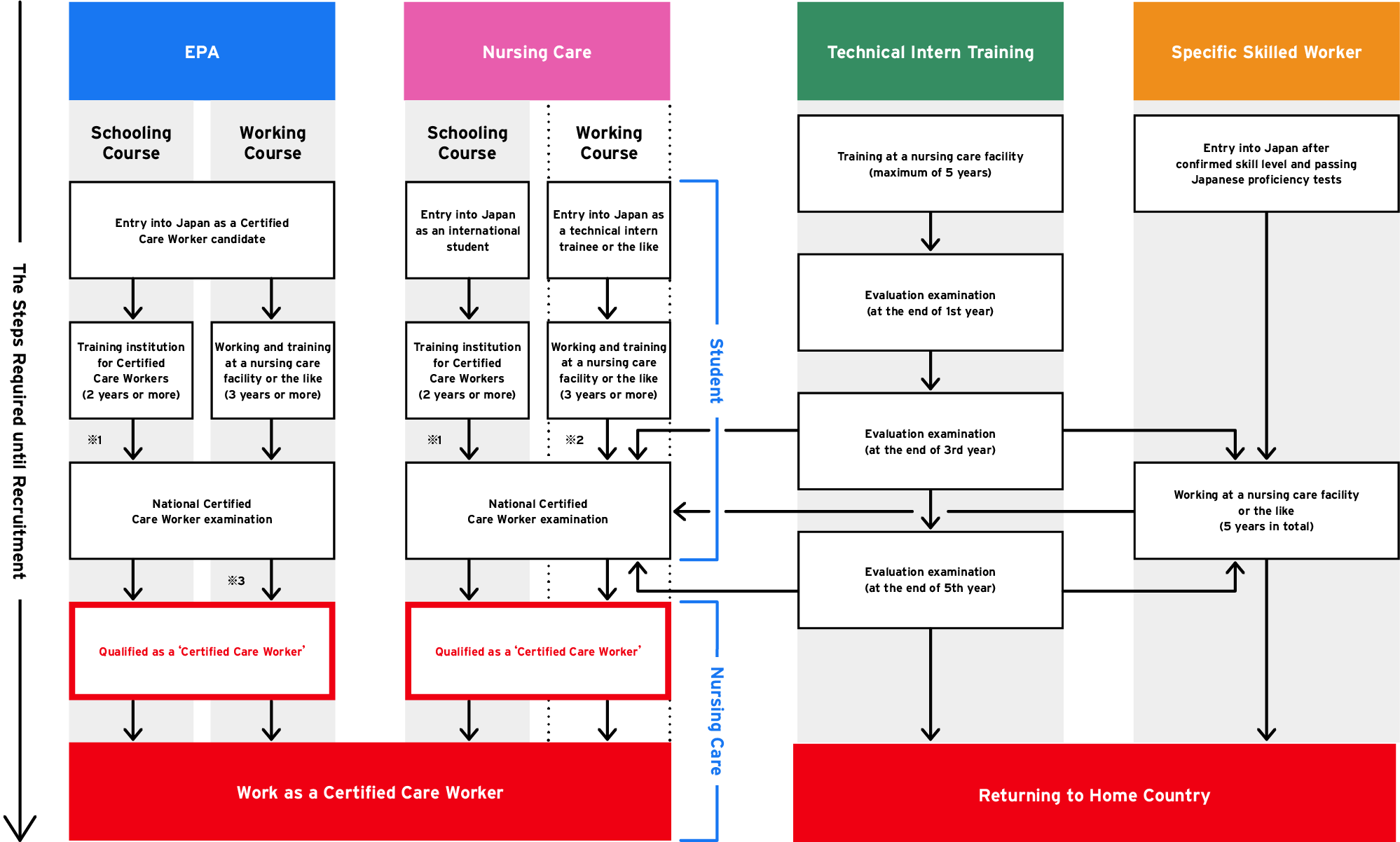
- ※1Graduates between April 2017 and March 2022 are required to pass the national examination within five years, or engage in long-term care for five years after graduation.
- ※2 The course within the dotted lines is to be established in the future.
- ※3Those who entered into Japan as EPA Certified Care Worker candidates and worked or trained appropriately for four years are exempted from skill test and Japanese proficiency test which are required for qualification as a Specific Skilled Worker (i).